A capital market is a system where savings and investments are mobilized by capital suppliers and consumers of such capital. Various entities buy or sell multiple financial instruments and products.
The capital market is the source of finance for companies and investment opportunities for investors.
Stocks (Equity securities) and Bonds (Debt Securities) of various companies are bought and sold by the investors and the general public in the capital market.
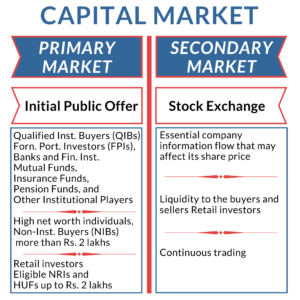
Other than the distinction between equity and debt, capital markets are also generally divided into two categories of markets:
The primary market is the new shares/paper issue market. It deals with the creation of new securities. Company issues equity shares to the public for the first time for raising capital resources is called Initial Public Offer (IPO). New shareholders will be able to participate in contributing to the capital of a company. The functions of the Primary Market are Origination, Underwriting, and Distribution of the share.
The shares were issued to the public through an initial public offer. Or the select group of investors in a private placement. A public proposal is open to three categories of investors:
A primary market issuance can also issue to a defined group of investors or private placement. A private investment made by a listed company is called a Preferential Allotment. A preferential allotment made to identified Qualified Institutional Buyers (QIB) is called a Qualified Institutional Placement.
Such an offer for sale does not increase or decrease the share capital of the company.
A secondary market is a place where trading takes place in the stock exchange or stock market for existing securities. Securities are bought and sold by investors in the secondary market or stock market. Functions of the secondary market are:
The leading stock exchanges in India are the National Stock Exchange (NSE), the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), and the Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India Ltd (MSEI).
